การจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง ตอนที่ 101.
First revision: Mar.03, 2022
Last change: Aug.30, 2023
สืบค้น รวบรวม เรียบเรียง และปริวรรต โดย อภิรักษ์ กาญจนคงคา.
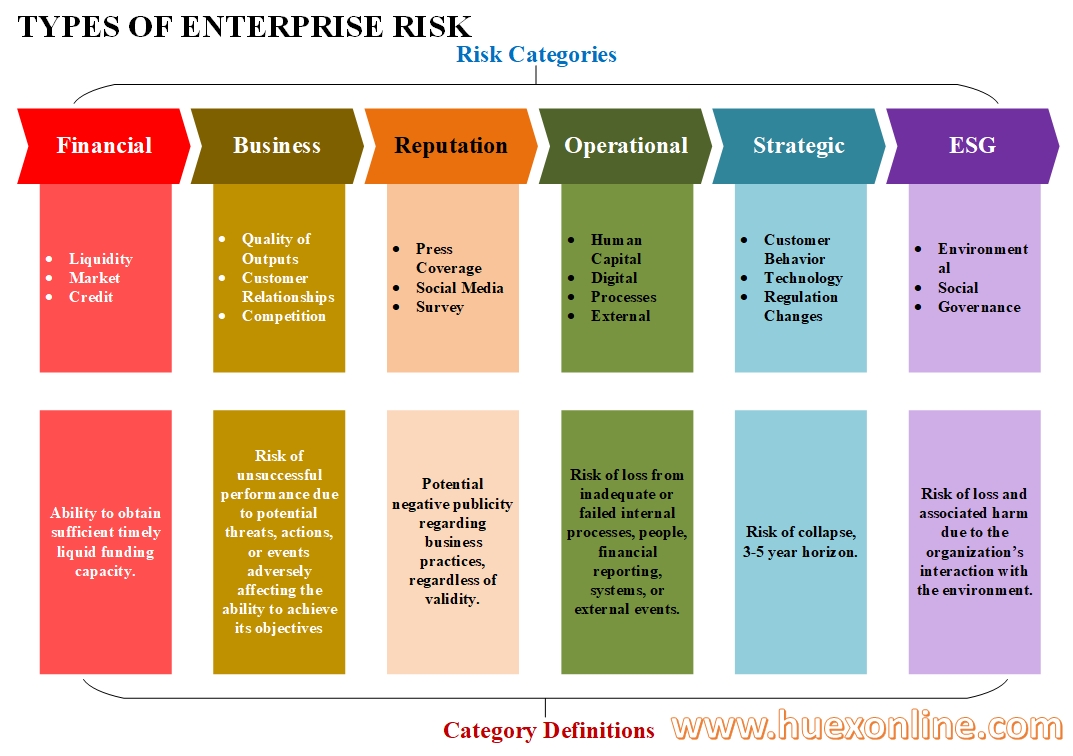
การจัดการความเสี่ยงขององค์กร (Type of Enterprise Risk)
1. ความเสี่ยงด้านการเงิน (Financial Risk)
- ความเสี่ยงจากการตลาด
- ความเสี่ยงจากการเกิดหนี้สูญ
- ความเสี่ยงของการให้เครดิต
2. ความเสี่ยงทางธุรกิจ (Business Risk)
- ความเสี่ยงจากคู่แข่งขัน
- ความเสี่ยงจากความสัมพันธ์กับลูกค้า
- ความเสี่ยงจากคุณภาพของผลิตภัณฑ์ ความเสี่ยงจากผลิตภัณฑ์ที่ไม่บรรลุความต้องการของลูกค้า
3. ความเสี่ยงด้านชื่อเสียง (Reputation Risk)
- ความเสี่ยงจากข้อมูลป้อนกลับในโซเชียลมีเดีย (Feedback Social Media)
- ความเสี่ยงจากผลสำรวจความพึงพอใจลูกค้า ข้อร้องเรียนลูกค้า
4. ความเสี่ยงจากการดำเนินงาน (Operations Risk)
- ความเสี่ยงด้านทรัพยากรมนุษย์
- ความเสี่ยงจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงสู่ระบบ Digitals
- ความเสี่ยงจากการขาดระบบการควบคุมทั้งภายในและภายนอก
5. ความเสี่ยงด้านกลยุทธ์ (Strategic Risk)
- ความเสี่ยงจากกฎระเบียบ กฎหมายที่เปลี่ยนแปลง
- ความเสี่ยงจากการเปลี่ยนแปลงเทคโนโลยี
6. ความเสี่ยงจากสภาพแวดล้อม สังคม ธรรมาภิบาล (Environmental, Social, and Governance Risk - ESG Risk)
- ความเสี่ยงจากความไม่สอดคล้องกับ ESG ทำให้ลูกค้า ผู้มีส่วนได้เสียไม่ยอมรับ
เนื้อหาของการจัดการความเสี่ยง สามารถแบ่งออกได้ดังนี้:
เกริ่นนำ (Foreword)
ส่วนที่หนึ่ง: บทนำการจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Introduction to risk management)
ส่วนที่สอง: การจัดการความเสี่ยงระดับกิจการ (Enterprise risk management)
ส่วนที่สาม: การประเมินและการวิเคราะห์ (Assessment and analysis)
ส่วนที่สี่: การสนองตอบต่อความเสี่ยง (Risk response)
ส่วนที่ห้า: สภาพแวดล้อมขององค์กร (Organizational environment)
ส่วนที่หก: กลยุทธ์ด้านความเสี่ยงและวัฒนธรรม (Risk strategy and culture)
ส่วนที่เจ็ด: การกำกับดูแลกิจการที่ดีของกิจการและการจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Corporate governance and risk management) และ
ส่วนที่แปด: การประกันความเสี่ยงและการรายงาน (Risk assurance and reporting).
โดยในบทเกริ่นนำและส่วนทั้งแปดนั้น มีรายละเอียดย่อยในแต่ละส่วนดังนี้
เกริ่นนำ (Foreword)
- บริบทการจัดการความเสี่ยง (Risk management in context)
- ลักษณะของความเสี่ยง (Nature of risk)
- การจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Risk management)
- คำศัพท์การจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Risk management terminology)
- ประโยชน์การจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Benefits of risk management)
- คุณสมบัติของการจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Features of risk management)
- โครงสร้างของบล็อกนี้ (This blog structure)
- การจัดการความเสี่ยงในทางปฏิบัติ (Risk management in practice)
- อนาคตของการจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Future of risk management)
ส่วนที่หนึ่ง: บทนำการจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Introduction to risk management)
- ผลลัพท์จากการเรียนรู้ (Learning outcomes)
- สิ่งที่ความศึกษาต่อไป (Further reading)
- กรณีศึกษา (Case studies)
01 What risk is and why it is important
- Definitions of risk
- Types of risks
- Risk description
- Levels of risk
- Classification systems
- Risk likelihood and impact
- Why understanding risk is important
- Impact of hazard risks
- Attachment of risks
- Risk and reward
- Attitudes to risk
- Risk and triggers
02 Risk is an opportunity as well as a threat
- Four types of risk
- Timescale of risk impact
- Minimize compliance risks
- Mitigate hazard risks
- Manage uncertainty (or control) risks
- Embrace opportunity risks
03 Managing risk: The background, principles, and aims of risk management.
- Origins of risk management
- Taking calculated risks
- Specialist areas of risk management
- Enterprise risk management
- Levels of risk management sophistication
- Principles of risk management
- Objectives of risk management
- Risk management activities
- Effective and efficient core processes
- Implementing risk management
- Achieving benefits
- Risk management drives and enables activities
04 Risk management standards
- Use of risk management standards for listed companies
- Risk management process
- Context
- The standard in more detail
- Updating of RM terminology
05 Risk management in context
- Scope of the context
- External context
- Internal context
- Risk management context
- Designing a risk register
- Using risk register
- The future of Risk registers
ส่วนที่สอง: การจัดการความเสี่ยงระดับกิจการ (Enterprise risk management)
- Learning outcomes
- Further reading
- Case studies
06 Enterprise risk management
- Enterprise-wide approach
- Definitions of ERM
- ERM in practice
- ERM and business continuity management
- Integrating strategy and performance
07 Implementing enterprise risk management
- Investment in change
- A worthwhile change
- Integrating processes, reviewing and improving
- Plan, implement, measure, and learn (PIML)
08 The Context for ERM
- Changing the face of risk management
- Lessons from the past: Financial and health crisis
- The power of taking risks
- Managing emerging risks
- The increasing importance of resilience
09 Setting objectives for ERM
- Risk management standards and objectives
- Strategy and objectives in standards
- Implementing objectives
- Aligning objectives to risk management principles
ส่วนที่สาม: การประเมินและการวิเคราะห์ (Assessment and analysis)
- Learning outcomes
- Further reading
- Case studies
10 Assessing risks: Consudearions, causes, and consequences
- Importance of risk assessment
- Approaches to risk assessment
- Risk assessment techniques
- Nature of the risk matrix
- Risk perception
- Attitude to risk
11 Classifying risks
- Risk classification systems
- Time to impact
- Examples of risk classification systems
- FIRM risk scorecard
- PESTLE risk classification system
- Compliance, hazard, control, and opportunity
12 Analysing risks: The dimensions of risk
- Levels of risk
- The inherent and current level of risk
- Control confidence
- 4Ts of hazard risk response
- Risk significance
- Risk capacity
- Evaluating risk: Risk appetite
13 Controlling the downside of risk
- Risk likelihood
- Risk magnitude
- Hazard risks
- Loss Prevention
- Damage Imitation
- Cost containment
14 Maximizing the upside of risk
- Defining the upside
- Opportunity assessment
- Riskiness index
- Upside in strategy
- Upside in projects/programs
- Upside in operations
- The upside of compliance risks
ส่วนที่สี่: การสนองตอบต่อความเสี่ยง (Risk response)
- Learning outcomes
- Further reading
- Case studies
15 Managing and responding to risk
- The 4Ts of Hazard Response
- Strategic risk response
16 Risk treatment controls for hazard risks
- Types of controls
- Cost of risk controls
17 Ongoing monitoring and review
- The importance of monitoring
- Frequency
- Process
- Reporting
- Responsibility
18 Insurance and risk transfer
- History of Insurance
- Transferring the financial consequences of risk
- Types of insurance cover
- Evaluation of insurance needs
- Purchase of insurance
- Captive insurance companies
19 Surviving shocks and disruption: ERM, BCP and resilience
- VUCA
- Business continuity planning and resilience
- Business continuity planning
- Business continuity standards
- Successful business continuity
- Business impact analysis
- Resilience, business continuity, and ERM
- Civil emergencies
ส่วนที่ห้า: สภาพแวดล้อมขององค์กร (Organizational environment)
- Learning outcomes
- Further reading
- Case studies
20 Business and the risk environment
- Dynamic business models
- Types of business processes
- Strategy and tactics
- Effective and efficient operations
- Ensuring compliance
- Reporting performance
21 The organization's business model, visions and values
- Components of the business model
- Risk management and the business model
- Ethics and corporate governance
- CSR and risk management
- Supply chain and ethical trading
- Importance of reputation
22 How risk management adds value
- What is the evidence?
- Improves performance and key risk indicators
- The benefits of an ERM approach
- Climate change as a key risk
- Becoming more strategic
ส่วนที่หก: กลยุทธ์ด้านความเสี่ยงและวัฒนธรรม (Risk strategy and culture)
- Learning outcomes
- Further reading
- Case studies
23 Risk architecture and strategy
- Architecture, strategy, and protocols
- Risk architecture
- Risk management strategy
- Risk management protocols
- Risk management manual
- Risk management documentation
24 Roles, responsibilities, and documentation
- Allocation of responsibilities
- Range of responsibilities
- Statutory responsibilities of management
- Role of the Risk Manager
- Risk Architecture in practice
- Risk committees
25 Culture and behaviors
- Styles of risk management
- Steps to successful risk management
- Defining risk culture
- Measuring risk culture
- Alignment of activities
- Risk maturity models
26 Risk appetite and tolerance
- Nature of risk appetite
- Risk appetite and the risk matrix
- Risk and uncertainty
- Risk exposure and risk capacity
- Risk appetite statements
- Risk appetite and lifestyle decisions
27 Risk training and communication
- Consistent response to risk
- Risk training and risk culture
- Risk information and communication
- Shared risk vocabulary
- Technology to support risk management processes and procedures
- Risk management information systems
28 Risk practitioner competencies
- Competency frameworks
- Range of skills
- Communication skills
- Relationship skills
- Analytical skills
- Management skills
ส่วนที่เจ็ด: การกำกับดูแลกิจการที่ดีของกิจการและการจัดการด้านความเสี่ยง (Corporate governance and risk management)
- Learning outcomes
- Further reading
- Case studies
29 Introducing corporate governance
- Corporate governance
- OECD principles of corporate governance
- The future direction of corporate governance
- London Stock Exchange corporate governance framework
- Corporate governance for a financial services organization
- Corporate governance for a government agency
- Evaluation of board performance
30 Stakeholders, ethics and corporate social responsibility
- Range of stakeholders
- Stakeholder dialogue
- Stakeholders and core processes
- Stakeholders and strategy
- Stakeholders and tactics
- Stakeholders and operations
31 Different approaches to risk management
- Operational risk management
- Project risk management
- Supply chain risk management
ส่วนที่แปด: การประกันความเสี่ยงและการรายงาน (Risk assurance and reporting)
- Learning outcomes
- Further reading
- Case studies
32 The control environment
- Nature of internal control
- The resilience of the organization in the event of external shock
- Purpose of internal control
- Control environment
- Features of the control environment
- Expectations of internal control
- CoCo framework of internal control
- Good safety culture
- The future of control processes
33 Internal audit activities
- Scope of internal audit
- Role of Internal Audit
- Undertaking an internal audit
- Risk management and internal audit
- Management responsibilities
- Five lines of assurance
34 Risk assurance techniques
- Audit committees
- Role of risk management
- Risk assurance
- Risk management outputs
- Control risk self-assessment
- Benefits of risk assurance
35 Reporting on risk management
- Risk reporting
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act 2002
- Risk reports by US companies
- Charities' risk reporting
- Public sector risk reporting
- Government report on national security
ที่มา คำศัพท์ และคำอธิบาย:
01. จาก. Fundamentals of Risk Management: Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Enterprise Risk Management, โดย Paul Hopkin และ Clive Thompson, ISBN-978-1398602861 สำนักพิมพ์ Kogan Page, พิมพ์ครั้ง 6, ธันวาคม 2564.



