Title Thumbnail & Hero Image: ที่มา: www.pinterest.com, วันที่เข้าถึง: 15 มิถุนายน 2568.
แผนความมั่นคงปลอดภัยด้านเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศ 2
First revision: Jun.15, 2025
Last change: Aug.24, 2025
สืบค้น รวบรวม เรียบเรียง แปล และปริวรรตโดย อภิรักษ์ กาญจนคงคา.
1.
หน้าที่ 1
1.
ส่วนที่ 2
การวางแผนความมั่นคงปลอดภัยเชิงกลยุทธ์ (Strategic Security Planning)
4. Managing Risk
- The Three Pilars of Security
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
4.1 Risk Management Overview
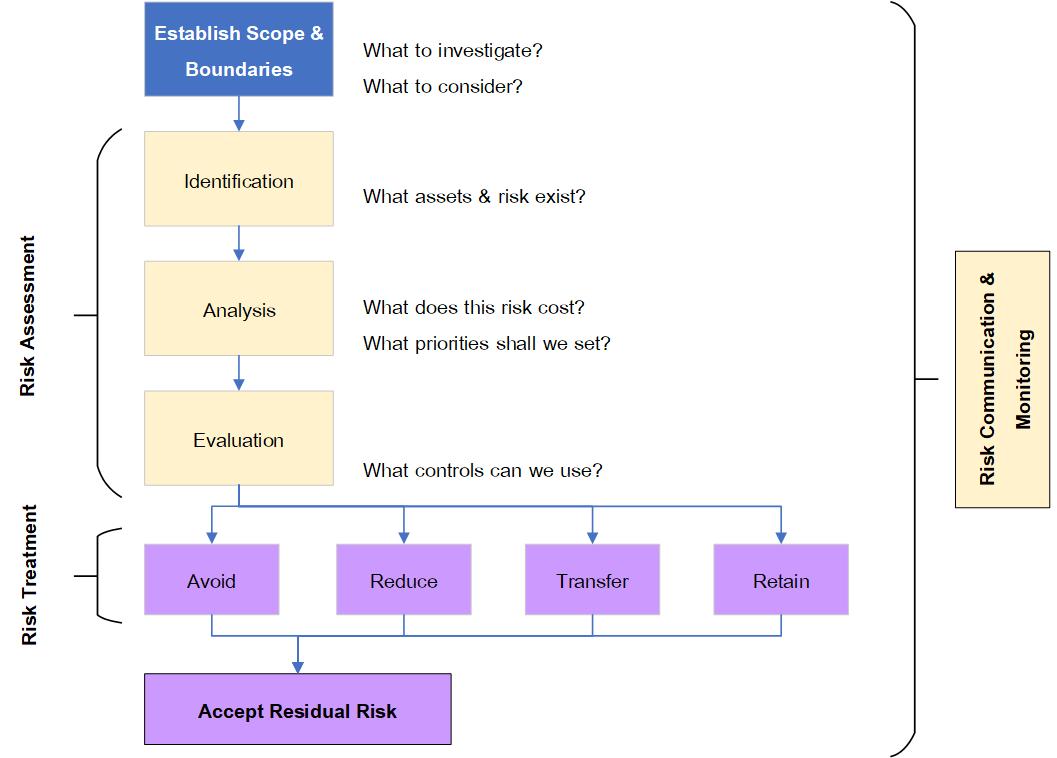
Fig. 4.1 Stages of Risk Management.
1.
- Risk Management - Analyzes the risks the organization is likely to face.
- Risk Treatment - Implements controls to reduce risks to acceptable levels.
- Residual Risk is the risk that remains after our control and avoidance implementations.
1.
2.
หน้าที่ 2
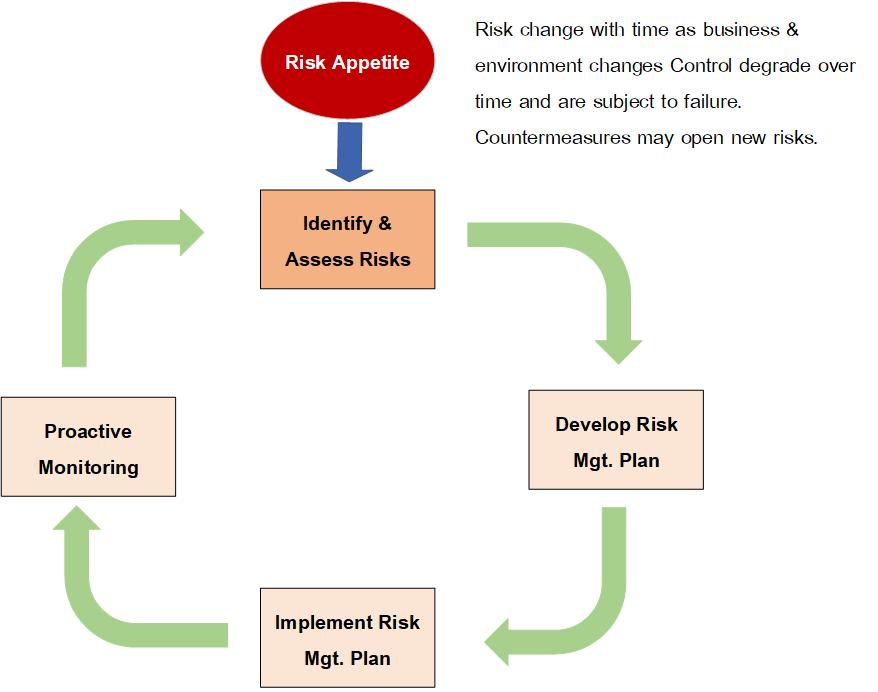
วงจรชีวิตด้านความมั่นคงปลอดภัย (The Security Lifecycle)
- วงจรชีวิตด้านความมั่นคงปลอดภัย (The Security Lifecycle) is know as กระบวนการจัดการความเสี่ยงอย่างต่อเนื่อง (The Continuous Risk Management Process).
Fig. 4.2 กระบวนการจัดการความเสี่ยงอย่างต่อเนื่อง (Continuous Risk Management Process).
1.
4.1.1. Step 1: ระบุความเสี่ยง (Identify Risks)
- ระบุสิ่งที่สำคัญที่สุดในองค์กร = IT, Database, Product, Cash, Reputation.
- คำถามสำคัญในการพิจารณาว่าอะไรคือทรัพย์สิน (Asset) ที่สำคัญขององค์กร:
- What is the value of this asset to our company?
- How Much does this asset contribute to our income?
- How much would it cost to recover or replace this asset?
- How much might we be liable for, if this asset were compromised?
- The Three Pillars of Security
- Confidentiality - ความเป็นที่เชื่อถือ มีความปลอดภัยเป็นความลับเฉพาะองค์กร.
- Integrity - ซื่อสัตย์ บูรณาการ มั่นคง.
- Availability - มีความพร้อมใช้งาน สามารถหามาได้.
- Tangible Costs = Cost of loss of integrity + Cost of loss of availability + Cost of loss of confidentiality.
- Risk Analysis - consists of the next three steps, which include analyzing threat, and vulnerabilities; estimating likelihood of exploitation; and computinh effective losses.
1.
2.
หน้าที่ 3
4.1.2. Step 2: Determine Loss Due to Threats.
- Vulnerable = เปราะบาง อ่อนแอ.
- Physical Threats = ภัยธรรมชาติ.
- Non-Physical Threat
- Ethical/Crimed: Fraud, การจารกรรม (Espinage), hacking, identity theft, malicious code, social engineering, vandalism, phlishing, and deniel of serice.
- External Environmental: industry competition, or changes in market, political, regulatory or technology environment.
- InternalL management error, IT complexity, poor risk evaluation, organization immaturit, accidental data loss, mistakes, software defects and personal incompetence.
1.
2.
4.1.3. Step 3: Estimate Likelihood of Exploitation.
- ต้องระวังเรื่อง Payment Cards, Financial credentials, and Bank Account Information.
- File Server ต้องระวัง - Spear Phlishing, Stealing data (Password Information) and remote control of computers (Backdoors, botnet and rootkit).
4.1.4. Step 4: Compute Expected Loss.
- Quantitative Analysis --> use the Valnerability Assessment Quadrant Map.
- Quantitative Risk Assessment
- Single Loss Expectancy (SLE)
- Annual Rare Occurance (ARO)
- Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE)
- ALE = SLE * ARO
- Exposure faster
- SLE = Asset Value (AV) * Exposure Factor (EF)
1.
2.
หน้าที่ 4
Fig.4-5 Semi-Quantitative Risk Analysis
This technique estimate threats with five labels of impact and five levels of Likelihood.
1). Risk Acceptance: It is possible to ignore risk, if the risk exposure is negligible. We will handle any arising problem as neccessary. E.g.,: Snow-storm in Florida.
2). Risk Avoidance: Stop doing risky behavior altogether, such as eliminating the use of Social Security Numbers, and avoiding storage of Payment Card Numbers.
3). Risk Mitigation: Implement Control(s) that minimize vulnerability. Two approaches include minimizing likelihood and minimizing impact. Teaching security awareness and using a firewall and antivirus software would minimize likelihood, while developing an Incident Response Pla would minimize the impact of an attach.
4). Risk Transference: Pay someone to assume risk for you, such as purchasing insurance against the threat. This category is recommended for low-frequency, high-cost risks. While insurance can transfer the financial impact, it cannot transfer legal responsibility (which you retain).
--> Deterrent Controls discourage people from deviant behavior.
--> Compensating Control is used as weaker alternative when the recommneded control is infeasible.
1.
2.
หน้าที่ 5
Fig.4.6 Demonstrates that this residual risk should be a fraction of the original risk.
4.1.6. Step 6: Monitor (and Communicate) Risk
- Due Diliigence is the responsibility of doing careful risk assessment.
4.2 The Ethics of Risk
1.
2.
3.
4.3 Advanced: Financial Analysis with Business Risk
The Three Techniques:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Net Present Value
- Internal Rate of Return
1.
2.
3.
4.4 Advanced: Risk for Larger Organizations
1.
2.
3.
Fig. 4.7 NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) risk assessment methodology