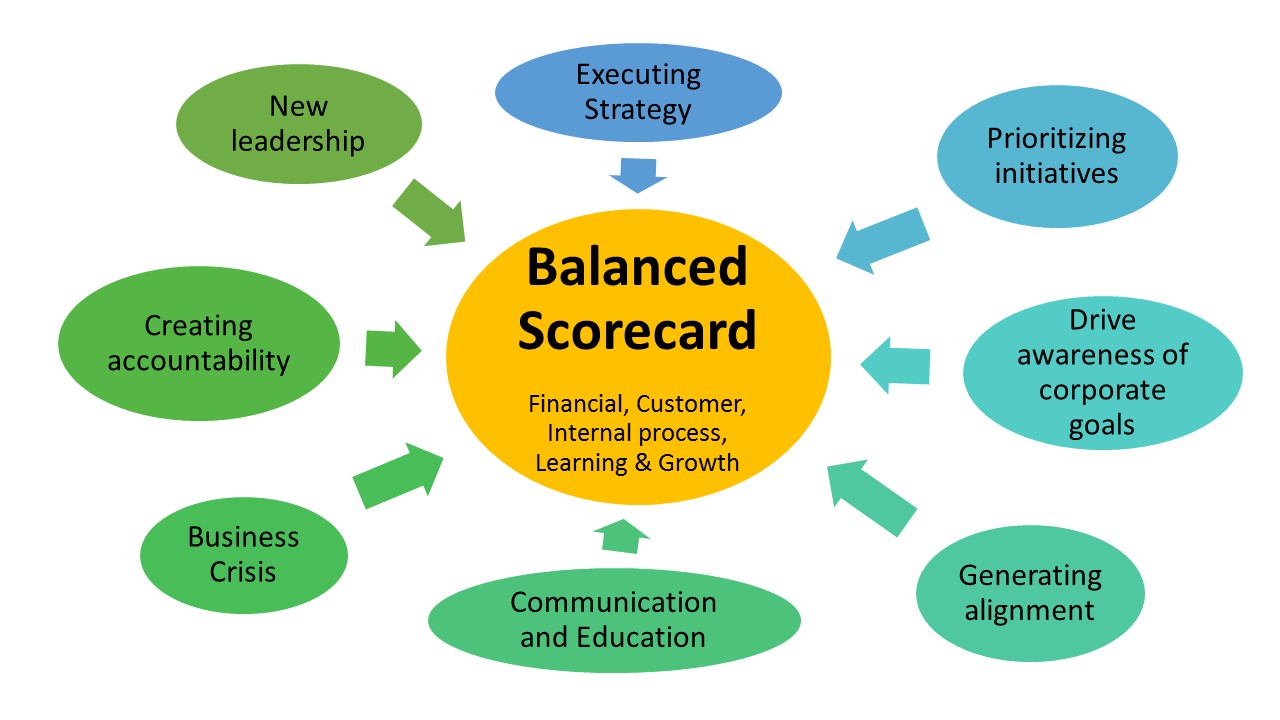
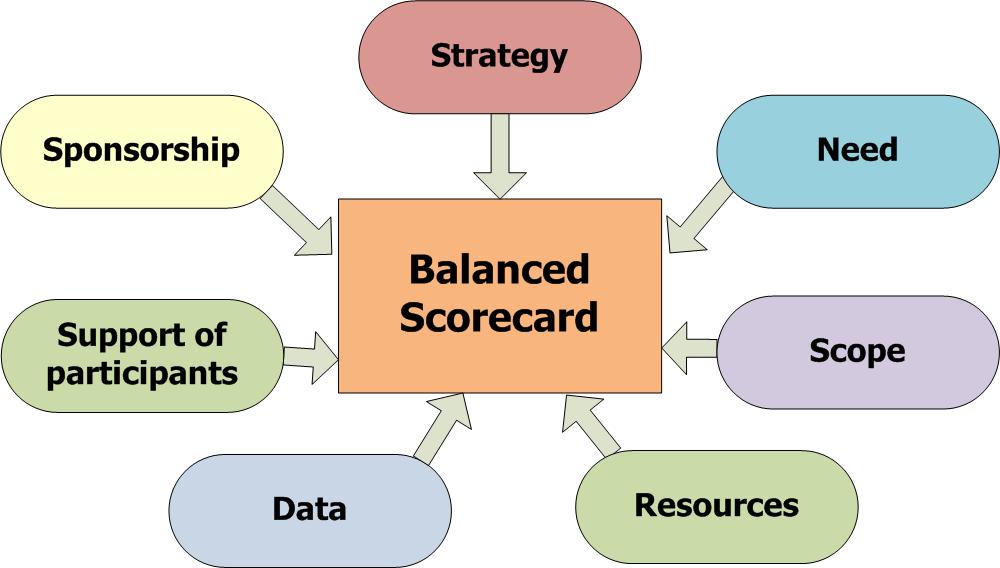
| บาล้านซ์สกอร์การ์ด หรือ บีเอสซี (Balanced Scorecard-BSC) |
- เป็นระบบรวบยอดที่ประมวลสำหรับการอธิบายและการแปลงกลยุทธ์ โดยผ่านการเชื่อมโยงวัตถุประสงค์การดำเนินงาน, ตัววัดค่าหรือมาตรการหรือตัวชี้วัด, เป้าหมาย, และสิ่งที่จะทำให้บรรลุเป้าหมายในมุมมองทั้งสี่, ลูกค้า, กระบวนการภายใน, การเงิน, และการเรียนรู้และการเติบโต. BSC แสดงบทบาทในฐานะที่เป็น ระบบการวัดค่า, ระบบการจัดการเชิงกลยุทธ์, และเครื่องมือสื่อสาร.
- An integrated system for describing and translating strategy through the use of linked performance objectives, measures, targets, and strategic initiatives in four, balanced perspectives - customer, internal process, financial, and learning and growth. The Balanced Scorecard acts as a measurement system, strategic management system, and communication tool. |
สิ่งที่จะทำให้บรรลุเป้าหมาย
(Initiatives) |
- สิ่งที่จะทำให้บรรลุเป้าหมายเชิงกลยุทธ์ (มักจะเรียกกันง่าย ๆ กรอบวงการ BSC ว่า อินนิชิทีฟ - initiatives) คือโครงการเฉพาะกิจ, กิจกรรม, หรือ โปรแกรม ที่เราจะเริ่มดำเนินการเพื่อบรรลุหรือเกินกว่าเป้าหมายที่วางไว้.
- Strategic initiatives (Often simply referred to as initiatives in the Scorecard vernacular) are the specific projects, activities, or programs we'll embark upon in order meet or exceed our performance targets. |
ตัวชี้วัดเบื้องหลัง -
(Lagging Indicator) |
- การวัดค่าผลการดำเนินงานนั้น เป็นตัวแทนของกิจกรรมต่าง ๆ ที่มีการเรียงลำดับไว้ก่อนแล้ว ได้นำมาอ้างอิงในฐานะที่เป็นตัวชี้วัดเบื้องหลัง. ได้มีการเน้นกันไว้บ่อย ๆ ถึงผลของช่วงเวลาที่สิ้นสุดลงและคุณลักษณะเฉพาะของการดำเนินงานที่ผ่านมา. ความพึงพอใจของพนักงานอาจจะพิจารณาได้ว่าเป็นตัวชี้วัดเบื้องหลัง. BSC ที่ดีจะต้องมีการประสมประสานทั้งตัวชี้วัดเบื้องหลังและด้านหน้า.
- Performance measures that represent the consequences of actions previously taken are referred to as lag indicators. They frequently focus on results at the end of a time period and characterize historical performance. Employee satisfaction may be considered a lag indicator. A good Balanced Scorecard must contain a mix of lag and leading indicators. |
| ตัวชี้วัด Lead - (Leading Indicator) |
- ตัวชี้วัดนี้ถูกเพ็งมองจากตัวชี้วัดเบื้องหลัง มีการสมมติถึงความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างสองตัวชี้วัด, โดยตัวชี้วัดที่ให้ข้อแนะนำให้การปรับปรุงผลการดำเนินงานนั้นคือ Leading indicator ซึ่งเป็นตัวชี้วัดที่จะให้ผลการดำเนินงานได้ดีกว่า Lagging indicator. ตัวอย่าง, อัตราการลาขาดที่ลดต่ำลง (Leading indicator) ได้ถูกสมมุติฐานว่าเป็นการขับเคลื่อนการสร้างความพึงพอใจให้กับพนักงาน (Lagging indicator).
- These measures are considered the drivers of lagging indicators. There is an assumed relationship between the two, which suggests that improved performance in a leading indicator will drive better performance in the lagging indicator. For example, lowering absenteeism (a leading indicator) is hypothesized to drive improvements in employee satisfaction (a lagging indicator). |
| ตัววัดค่า - Measure |
- เป็นการใช้ที่มีมาตรฐานในการประเมินและสื่อสารผลการดำเนินงาน เทียบกับผลลัพธ์ที่คาดหวัง. ตัววัดค่านี้ โดยปกติมีลักษณะเป็นเชิงปริมาณ แสดงในรูปของตัวเลข, หน่วยเงินตรา, ร้อยละ, และอื่น ๆ . การรายงานและการติดตามด้วยตัววัดค่านี้ จะช่วยเป็นมาตรวัดให้องค์กรให้เห็นถึงความก้าวหน้าการดำเนินงานด้วยกลยุทธ์อย่างมีประสิทธิผล.
- A standard used to evaluate and communicate performance against expected results. Measures are normally quantitative in nature capturing numbers, dollars, percentages, and so on. Reporting and monitoring measures helps an organization gauge progress toward effective implementation of strategy. |
| ถ้อยแถลงพันธกิจ - Mission Statement |
- ถ้อยแถลงพันธกิจ จะแสดงถึงวัตถุประสงค์หลักขององค์กรว่า - เหตุใดเล่าเราถึงธำรงอยู่. พันธกิจจะตรวจสอบเหตุผลในการธำรงอยู่สำหรับองค์กี และสะท้อนถึงแรงจูงใจของพนักงานที่ผูกพันการภาระงานขององค์กร. พันธกิจที่มีประสิทธิผลนั้นดลใจ, ยั่งยืน, เข้าใจง่าย, และง่ายในการสื่อสาร.
- A mission statement defines the core purpose of the organization-why it exists. The mission examines the (รีออน เดท) - Raison d'être for the organization and reflects employees' motivations for engaging in the organization's work. Effective missions are inspiring, long term in nature, and easily understood and communicated. |
| วัตถุประสงค์ - Objective |
- วัตถุประสงค์เป็นข้อความกระชับแสดงถึงสิ่งที่องค์กรจะต้องทำให้ดีในแต่ละมุมมองที่เป็นด้านการเงิน, ลูกค้า, กระบวนการภายใน, และการเรียนรู้และการเติบโต เพื่อที่จะดำเนินการด้วยกลยุทธ์ที่โดดเด่น. วัตถุประสงค์จะเริ่มด้วยคำกริยาเช่น เพิ่ม, ลด, ปรับปรุง บรรลุ, และอื่น ๆ . แผนที่กลยุทธ์ประกอบด้วยวัตถุประสงค์ (ทุก ๆ มุมมอง) ทั้งหมด.
- Objectives are concise statements of what the organization must do well in each of the four perspectives of financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth in order to execute its unique strategy. Objectives begin with verbs such as increase, reduce, improve achieve, and so on. Strategy maps are comprised entirely of objectives. |
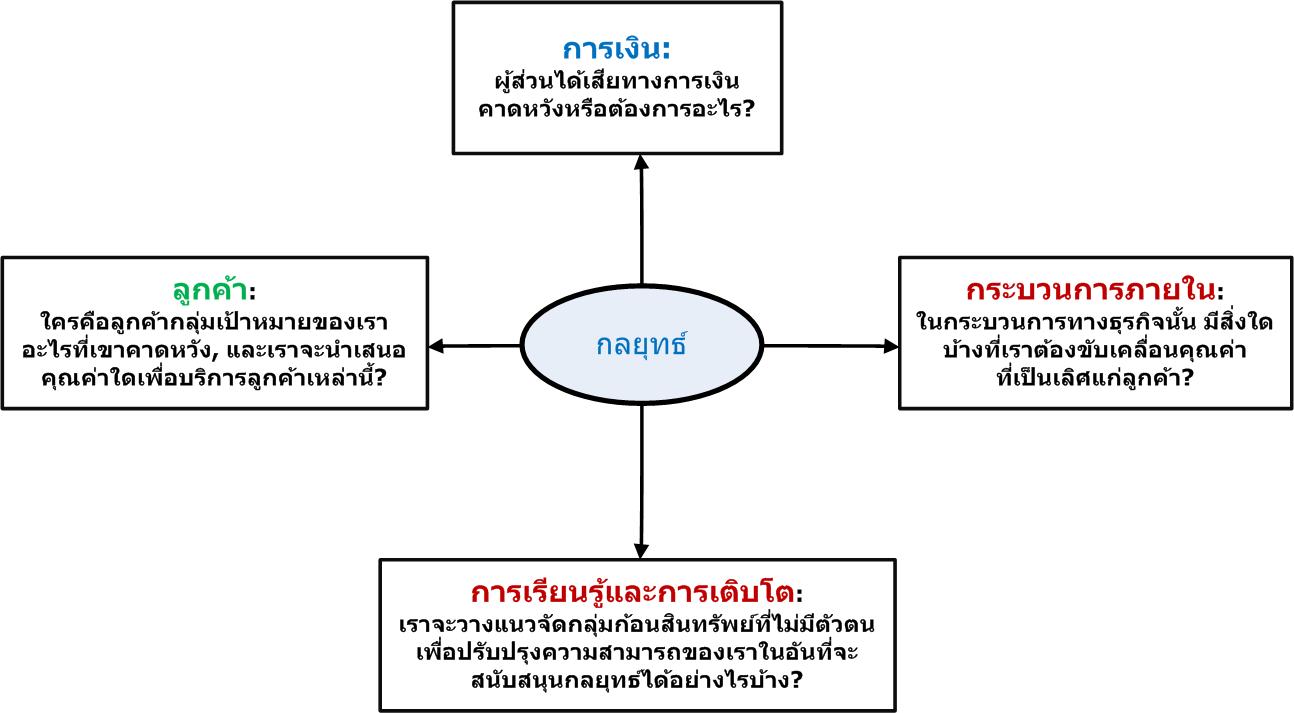
| มุมมอง - Perspective |
- ด้วยพื้นฐานของ BSC แล้ว, มุมมองได้อ้างอิงยังกลุ่มของวัตถุประสงค์หรือการวัดค่าการดำเนินงาน. องค์กรส่วนใหญ่ล้วนเลือกสี่มุมมองอันเป็นมาตรฐาน (การเงิน, ลูกค้า, กระบวนการภายใน, และการเรียนรู้และการเติบโต), อย่างไรก็ตาม, BSC นั้นเป็นตัวแทนของกรอบงานที่เป็นพลวัต, มุมมองที่เพิ่มขึ้นอาจจะมีได้ก็ด้วยความจำเป็น เพื่อให้เพียงพอต่อการอธิบายกลยุทธ์ขององค์กร.
- In Balanced Scorcard vernacular, perspective refers to a category of performance objectives or measures. Most organizations choose the standard four perspectives (financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth), however, the Balanced Scorecard represents a dynamic framework, and additional perspective may be added as necessary to adequately translate and describe an organization's strategy. |
ระบบการจัดการเชิงกลยุทธ์ -
Strategic management System |
- อธิบายถึงการใช้ BSC ที่ได้วางกรอบในกิจกรรมต่าง ๆ ตามกลยุทธ์ขององค์กรระยะสั้น. มักจะเสร็จลุล่วงด้วยการเรียงร้อย BSC ลงมาทุกระดับขององค์กร, วางกรอบงบประมาณและแผนธุรกิจต่าง ๆ ด้วยกลยุทธ์, และใช้ Scorecard เป็นกลไกในการย้อนข้อมูลกลับและเป็นการเรียนรู้.
- Describes the use of the Balanced Scorecard in aligning an organization's short-term actions with strategy. Often accomplished by cascading the Balanced Scorecard to all levels of the organization, aligning budgets and business plans to strategy, and using the Scorecard as a feedback and learning mechanism. |
การจัดสรรทรัพยากรเชิงกลยุทธ์ -
Strategic Resource Allocation |
- กระบวนการของงบประมาณที่ได้วางกรอบไว้ด้วยกลยุทธ์ ด้วยการใช้ BSC เพื่อใช้ในการตัดสินใจปันส่วนทรัพยากร. การใช้วิธีการนี้, งบประมาณต่าง ๆ อยู่บนความจำเป็นในการสิ่งที่จะทำให้บรรลุเป้าหมายนั้น ลุล่วงถึงเป้าหมาย BSC.
- The process of aligning budgets with strategy by using the Balanced Scorecard to make resources allocation decisions. Using this method, budgets are based on the initiatives necessary to archieve Balanced Scorecard targets. |
| กลยุทธ์ -Strategy |
- เป็นตัวแทนของความสำคัญก่อนหลังในมุมกว้างที่ประยุกต์จากองค์กรที่ตระหนักถึงสภาพแวดล้อมการทำงานและการมุ่งให้บรรลุตามพันธกิจขององค์กร. สภาพการณ์ในใจกลางของระบบ BSC, ทุกวัตถุประสงค์และตัววัดค่าต่าง ๆ นั้นจะต้องวางไว้ในกรอบกลยุทธ์ขององค์กร. กลยุทธ์ยังคงเป็นหนึ่งในประเด็นของการถกเถียงอย่างกว้างขวางในองค์สมัยใหม่ของโลก.
- Represents the broad priorities adopted by an organization in recognition of its operating environment and in pursuit of its mission. Situated at the center of the Balanced Scorecard system, all performance objectives and meausres should align with the organization's strategy. Strategy remains one of the most widely discussed and debated topics in the world of modern organizations. |
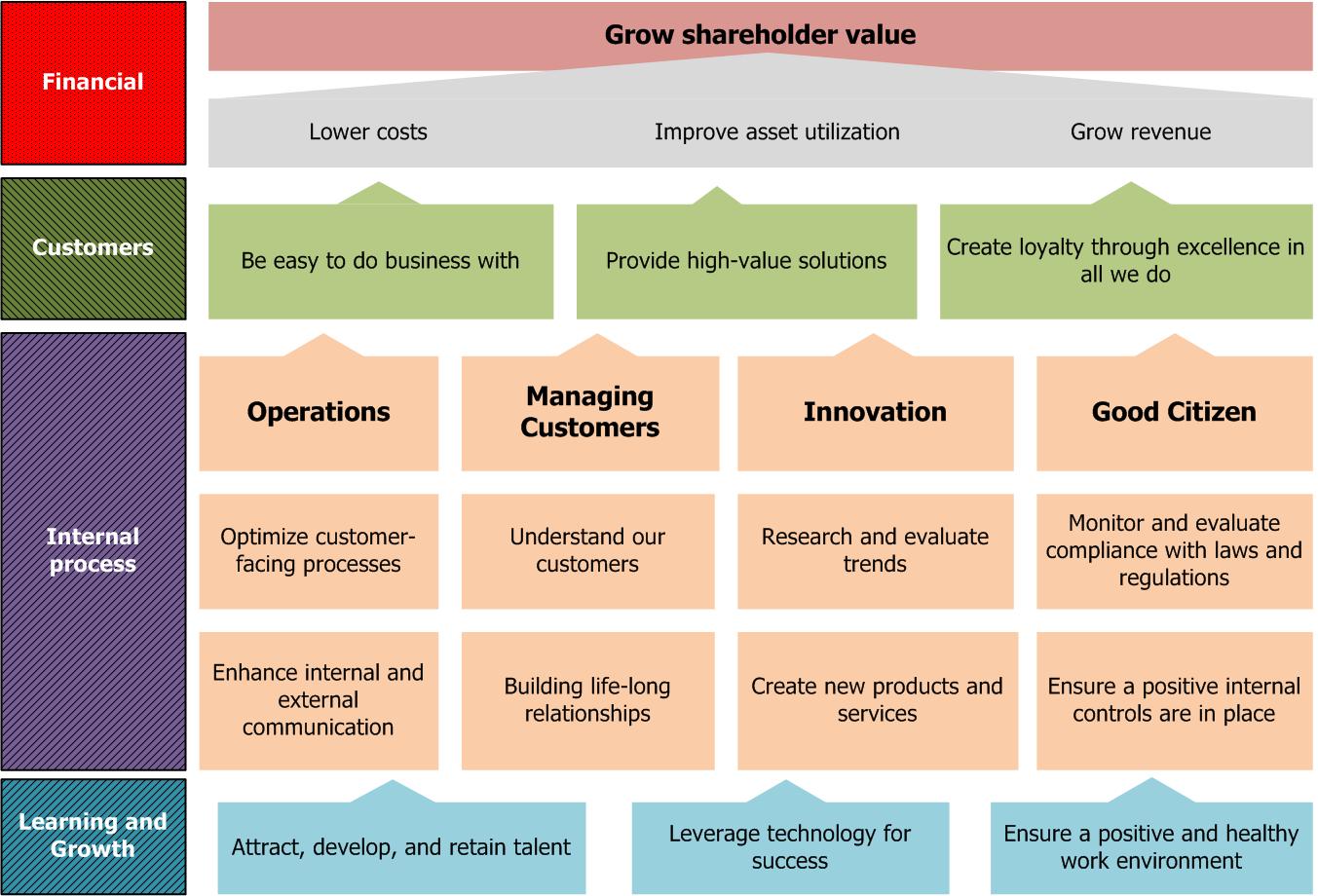
| แผนที่กลยุทธ์ - Strategy Map |
- การนำเสนอด้วยรายงานเพียงหน้าเดียว, กราฟิก ถึงสิ่งที่ได้ทำไว้สำเร็จในการนำกลยุทธ์ไปปฏิบัติ. แผนที่กลยุทธ์ประกอบด้วยวัตถุประสงค์การดำเนินงานที่วางขยายไปด้วยสี่มุมมองและเชื่อมโยงด้วยกัน เพื่อที่จะเล่าเรื่องราวด้านกลยุทธ์ขององค์กร.
- A one-page, graphical representation of what must be done well in order to execute strategy. Strategy maps are composed of performance objectives spanning the four perspectives and linking together to tell the organization's strategic story. |
| เป้าหมาย- Target |
- เป็นตัวแทนของผลลัพท์ที่ต้องการของการวัดผลการดำเนิน. เป้าหมายจะส่งข้อมูลย้อนกลางให้องค์ก์เกี่ยวกับผลการดำเนินงาน, ที่ชุ่มไปด้วยผลลัพท์ที่ได้มาจากตัววัดค่าที่มีนัยมีความหมาย.
- Represents the desired result of performance measure. Targets provide organizations with feedback regarding performance, and imbue the results derived from measurement with meaning. |
| การนำเสนอคุณค่า - Value Proposition |
- อธิบายว่าองค์กรนั้นมีความแตกต่างอย่างไรให้ลูกค้าทราบ, และอะไรคือกลุ่มคุณค่าที่เราจะส่งมอบ. เพื่อพัฒนาการนำเสนอคุณค่าแก่ลูกค้า โดยหลาย ๆ องค์กรได้เลือกหนึ่งในสามวินัยที่ประกบเรียงกันไป จากงานของทรีซี่และเวียร์สเซมาในหนังสือ "The Discipline of Market Leaders" ความเป็นเลิศด้านการดำเนินงาน, ความเป็นผู้นำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์, หรือการเข้าใจอย่างลึกซึ้งต่อลูกค้า.
- Describes how an organization will differentiate itself top customers, and what particular set of values it will deliver. To develop a customer value proposition many organizations will choose one of three disciplines articulated by Treacy and Wiersema in The Discipline of Market Leaders: operational excellence, product leadership, or customer intimacy. |
| วิสัยทัศน์ - Vision |
- ถ้อยแถลงด้านวิสัยทัศน์ได้ให้ภาพที่แสดงเป็นคำพูดออกมา ถึงสิ่งที่องค์กรโน้มที่จะเป็น - ซึ่งอาจจะห้า, สิบ, หรือ 15 ปีในอนาคตข้างหน้า. ถ้อยแถลงไม่ควรเป็นนามธรรม - ควรประกอบผนึกแน่นด้วยด้วยภาพของสถานะที่เราปรารถนา เท่าที่เป็นไปได้ และให้พื้นฐานให้ก่อร่างกลยุทธ์และวัตถุประสงค์ต่าง ๆ
- "A vision statement provides a word picture of what the organization intends to become - which may be 5, 10, or 15 years in the future. This statement should not be abstract - it should contain as concrete a picture of the desired state as possible and also provide the basis for formulating strategies and objectives." |